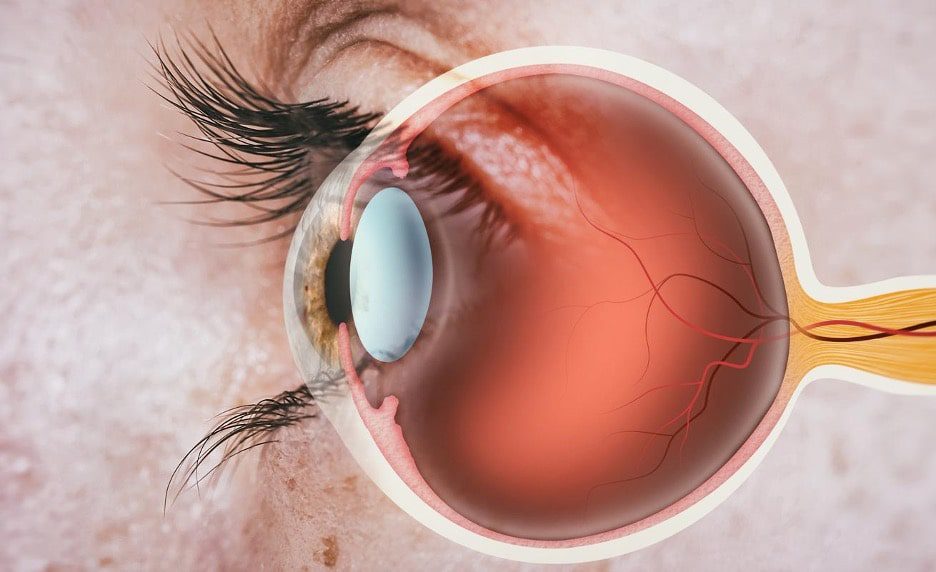
If you experience sudden vision changes or persistent spots in your field of view, seek immediate medical attention. Timely intervention is crucial in addressing retina problems that can lead to severe complications, including permanent vision loss.
Common issues affecting the retina include retinal detachment, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration. Each condition presents distinct symptoms and requires specific diagnostic approaches. For instance, retinal detachment often manifests as flashes of light or a curtain-like shadow over your vision, while diabetic retinopathy may not show clear symptoms until significant damage occurs.
Routine eye exams play a vital role in early detection. Regular screenings can identify changes in the retina that may signal underlying issues, allowing for prompt treatment. If you have diabetes or a family history of eye problems, prioritize these check-ups with your eye care professional.
Managing risk factors is crucial when it comes to preserving retina health. Controlling blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, and avoiding smoking significantly reduce the likelihood of developing retinal diseases. Keep an eye on changes in your vision, and consult your physician if you notice anything unusual.
- Understanding Retina Problems: A Comprehensive Guide
- Common Retina Conditions
- Preventive Measures
- Treatment Options
- Common Symptoms of Retina Issues
- Diagnosis Techniques for Retina Disorders
- Available Treatment Options for Retina Problems
- Preventive Measures for Maintaining Retina Health
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Avoiding Harmful Behaviors
Understanding Retina Problems: A Comprehensive Guide
Regular eye check-ups play a significant role in early detection of retina problems. If you notice blurred vision, floaters, or sudden changes in your sight, consult an eye specialist as soon as possible.
Retina problems can arise from various causes such as diabetes, high blood pressure, age-related macular degeneration, and retinal detachment. Recognizing symptoms early can lead to timely treatment and better outcomes.
Common Retina Conditions
- Diabetic Retinopathy: A diabetes complication affecting the eyes, leading to retinal damage. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial.
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Causes loss of central vision. Regular eye exams and a healthy diet may help mitigate risks.
- Retinal Detachment: A serious condition requiring immediate medical attention. Symptoms include sudden flashes of light and shadow in peripheral vision.
- Retinal Vascular Occlusion: Blockage of the blood vessels in the retina, resulting in sudden vision loss. Monitoring cardiovascular health is important.
Preventive Measures
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Control diabetes and blood pressure through regular monitoring and medication.
- Wear sunglasses that block UV rays to protect your eyes.
- Quit smoking, as it increases the risk of various eye diseases.
- Stay physically active to promote overall health.
Treatment Options
Treatment methods will depend on the specific condition:
- Laser Therapy: Used to treat conditions like diabetic retinopathy.
- Injections: Medications may be injected directly into the eye for conditions such as AMD.
- Surgery: In cases of retinal detachment, surgical intervention is often necessary.
- Monitoring: Some conditions may simply require regular monitoring without intervention.
Staying informed about retina problems contributes to eye health. Regular check-ups and a proactive approach to symptoms significantly improve vision outcomes. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
Common Symptoms of Retina Issues
Monitor your vision for changes that could signal retinal issues. Key symptoms include:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Blurry Vision | Experience a gradual or sudden blurriness in one or both eyes, which can affect daily activities. |
| Flashes of Light | See flashes or streaks of light, possibly indicating traction on the retina. |
| Floaters | Notice small spots or lines that drift across your vision, which may signal retinal changes. |
| Dark Shadows | Perceive dark patches or shadows in your field of vision, suggesting potential retinal detachment. |
| Color Distortion | Detect changes in how you perceive colors, which might indicate retinal issues. |
| Difficulty with Night Vision | Struggle to see in low light conditions, suggesting potential retinal problems. |
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult an eye care professional for further evaluation. Early diagnosis can prevent severe complications associated with retinal disorders.
Diagnosis Techniques for Retina Disorders
Fundus photography allows specialists to capture detailed images of the retina, aiding in the identification of various issues such as retinal detachments and diabetic retinopathy. This non-invasive technique provides a permanent record for future comparisons.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) delivers high-resolution cross-sectional images of retinal layers. This technique reveals subtle changes in the retina, making it invaluable for diagnosing macular degeneration and epiretinal membranes.
Fluorescein angiography enhances visualization of retinal blood vessels. By injecting a fluorescent dye, physicians can detect leaks and blockages in blood flow, crucial for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion.
Fundus autofluorescence detects changes in the retinal pigment epithelium. This technique helps in identifying conditions like retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration, providing insights into disease progression.
Electroretinography (ERG) measures the electrical responses of the retina’s photoreceptors. This test is valuable for diagnosing inherited retinal diseases and assessing retinal function.
Visual field testing evaluates the central and peripheral vision and helps detect abnormalities caused by retinal or optic nerve disorders, such as glaucoma.
Regular eye examinations, including these diagnostic techniques, enhance early detection and treatment of retinal disorders, significantly improving patient outcomes.
Available Treatment Options for Retina Problems
Laser therapy, such as photocoagulation, is a common option for treating retinal issues like diabetic retinopathy or retinal tears. This procedure aims to seal leaking blood vessels and prevent further damage by using focused light beams.
Intravitreal injections deliver medication directly into the eye. Anti-VEGF drugs, like Lucentis or Eylea, are frequently used to treat age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic eye diseases. These injections help minimize fluid leakage and reduce swelling.
For more severe conditions, surgery may be necessary. Vitrectomy involves removing the vitreous gel from the eye, allowing surgeons to address problems like retinal detachment or hemorrhage. This procedure often improves vision and stabilizes the retina.
Additionally, patients with geographic atrophy associated with AMD might benefit from nutritional supplements, such as those included in the AREDS formula. This combination of vitamins and minerals can slow progression in certain cases.
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential. Early detection and intervention play key roles in managing retina problems efficiently. Consult with an eye care professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach for your specific condition.
Preventive Measures for Maintaining Retina Health
Regular comprehensive eye exams play a key role in early detection of retinal issues. Schedule these annually, especially if you have a family history of eye diseases or conditions. Your eye care professional can conduct essential tests to monitor your retina’s condition.
Protect your eyes from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB light when outdoors. This simple step can reduce the risk of retinal damage over time.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids. Foods like leafy greens, spinach, kale, and fish contribute to retinal health. Consider adding foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, which combat oxidative stress.
Stay physically active to improve overall circulation, which supports eye health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week. This can include walking, swimming, or cycling.
Avoiding Harmful Behaviors
Quit smoking to significantly decrease your risk of developing retinal diseases. Studies show a strong connection between smoking and conditions such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Seek support if needed to help with this lifestyle change.
Limit screen time and practice the 20-20-20 rule. Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. This helps reduce digital eye strain, which can impact your retinal health over the long term.
Managing chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension is essential. Regular monitoring and adhering to treatment plans can prevent complications that may affect your retina. Stay informed and work closely with your healthcare provider.