For treating uterine infections, doxycycline hyclate is a reliable antibiotic option that targets the underlying bacteria effectively. This medication belongs to the tetracycline class, which inhibits bacterial protein synthesis, thereby stopping the growth of various pathogens associated with uterine infections. It is particularly useful against Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis, common culprits in these conditions.
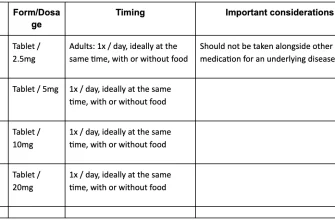
Typically prescribed in a dose of 100 mg twice daily for a period of 7 to 14 days, doxycycline can lead to significant improvement in symptoms. Patients often report reduced fever, decreased abdominal pain, and overall improvement in clinical signs within a few days of starting treatment. Always consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and to tailor treatment to individual needs.
It’s crucial to take doxycycline with a full glass of water and to avoid lying down for at least half an hour to prevent esophageal irritation. Additionally, this medication may cause photosensitivity, so taking precautions against sun exposure while on treatment is advisable. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider can ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and monitor for any potential side effects.
- Doxycycline Hyclate for Uterine Infection
- Dosing Recommendations
- Considerations and Precautions
- Understanding Uterine Infections and Their Impact
- Mechanism of Action of Doxycycline Hyclate
- Indications for Doxycycline in Uterine Infections
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Patients
- Potential Side Effects and Considerations
- Common Side Effects
- Serious Side Effects
Doxycycline Hyclate for Uterine Infection
Doxycycline hyclate serves as a powerful antibiotic choice for treating certain uterine infections. It’s particularly effective against bacterial pathogens that contribute to pelvic inflammatory disease and other reproductive system infections. Administering doxycycline improves recovery rates and reduces complications associated with these infections.
Dosing Recommendations
The typical dosage for treating uterine infections with doxycycline is 100 mg taken twice daily. This regimen usually lasts for 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s response to treatment. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate duration and dosage specific to your situation.
Considerations and Precautions
It’s essential to inform your doctor if you have a history of allergic reactions to tetracyclines or other antibiotics. Doxycycline is not recommended for pregnant women or children under the age of 8 due to the risk of teeth discoloration and potential effects on bone growth. Staying hydrated during treatment can also enhance absorption and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
Regular follow-up appointments help monitor treatment effectiveness and allow for adjustments if necessary. If symptoms persist or worsen, reevaluating the treatment plan is critical.
Understanding Uterine Infections and Their Impact
Uterine infections can lead to significant health issues if left untreated. Symptoms often include fever, abdominal pain, and unusual vaginal discharge. It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms early to facilitate prompt treatment.
Infections can stem from various causes, including retained tissue post-delivery, sexually transmitted infections, or complications after medical procedures. Proper diagnosis often involves a pelvic examination and lab tests to identify the specific pathogen responsible for the infection.
The impact of untreated uterine infections can extend beyond physical discomfort. They may lead to more serious conditions, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can result in infertility or chronic pain. Early intervention is key to preventing these complications.
Antibiotics like doxycycline hyclate are commonly prescribed to manage bacterial infections in the uterus. This medication effectively targets a variety of bacteria, allowing for quicker recovery and reduced risk of complications. Following the prescribed dosage and duration is essential for ensuring the infection does not recur.
Monitoring symptoms during treatment is important. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare provider is necessary to reassess the situation and consider alternative treatments. Maintaining communication with your healthcare team allows for adjustments in your care plan as needed.
Education on preventive measures can also reduce the risk of uterine infections. Regular gynecological check-ups, safe sexual practices, and proper postpartum care are all effective strategies for maintaining uterine health.
Mechanism of Action of Doxycycline Hyclate
Doxycycline hyclate operates primarily by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. It targets the 30S ribosomal subunit, preventing the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA to the mRNA-ribosome complex. This action disrupts the production of proteins essential for bacterial growth and reproduction, then effectively halting their proliferation.
This drug exhibits broad-spectrum activity against various gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as some atypical pathogens. The inhibition of protein synthesis not only halts microbial multiplication but also aids in the destabilization of the microbial cell membrane.
When treating uterine infections, doxycycline hyclate demonstrates its efficacy by addressing polymicrobial infections often associated with conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Its ability to penetrate tissues adequately ensures high local concentrations where infection may reside, enhancing its therapeutic effects.
| Bacterial Target | Action |
|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | Inhibition of protein synthesis |
| Gram-negative bacteria | Inhibition of protein synthesis |
| Atypical pathogens | Inhibition of protein synthesis |
Resistance can develop with improper use. Complying with prescribed dosages is crucial to minimize the emergence of resistant strains. Always consult healthcare professionals for tailored advice regarding dosage and duration of treatment when using doxycycline for uterine infections.
Indications for Doxycycline in Uterine Infections
Doxycycline serves as an antibiotic choice for the treatment of certain uterine infections, particularly those caused by susceptible bacteria. It is commonly indicated for endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and other gynecological infections where the presence of anaerobic bacteria is suspected.
In cases of endometritis, especially postpartum or post-abortion, doxycycline targets organisms like Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis, which often contribute to the infection. Administering doxycycline can facilitate a comprehensive approach when combined with other antibiotics to cover a broader spectrum of potential pathogens.
When managing PID, doxycycline is frequently part of a dual therapy regimen. It helps reduce inflammation and bacterial load, effectively treating the underlying infection while alleviating symptoms. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for patients with renal impairment, so monitoring renal function remains essential throughout treatment.
Doxycycline is also beneficial for chronic pelvic pain related to endometriosis when there is an infectious component. Addressing the infection with this antibiotic can help improve the patient’s overall condition and may reduce the risk of complications.
Monitoring for potential side effects, such as photosensitivity and gastrointestinal disturbances, is crucial. Avoiding sun exposure and ensuring proper hydration can minimize these risks. Always consider individual patient circumstances, including drug allergies and possible interactions with other medications, before initiating treatment.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Patients
For adults diagnosed with a uterine infection, the typical dosage of doxycycline hyclate is 100 mg taken twice daily. This administration should occur with a full glass of water to enhance absorption and reduce the risk of esophageal irritation.
It’s crucial to maintain consistent intake times. Taking the medication at the same time each day helps establish a routine, ensuring optimal effectiveness. Avoid taking doxycycline with dairy products, antacids, or iron supplements within two hours of each other, as these can interfere with absorption.
Monitor for side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. If these symptoms persist or worsen, contact your healthcare provider. It’s also advisable to complete the entire prescribed course, even if symptoms improve, to reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance.
For patients with renal impairment, dose adjustments may be necessary; consult your physician for personalized recommendations. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss the implications of doxycycline use with their healthcare provider due to potential risks.
Regular follow-up appointments are important to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and make necessary adjustments based on your health progress. If a dose is missed, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next dose. Do not double doses.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Doxycycline hyclate can lead to several side effects. Awareness of these effects assists in monitoring and managing them effectively.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Photosensitivity, increasing sunburn risk
- Skin rash or discoloration
Serious Side Effects
- Severe allergic reactions, including difficulty breathing
- Esophageal irritation or ulceration
- Changes in vision or blurred vision
- Persistent headache or dizziness
Consult a healthcare provider if any serious side effects occur. Inform them about all medications being taken, as doxycycline may interact with certain antibiotics and oral contraceptives. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should avoid doxycycline due to potential harm to the developing fetus or infant.
Maintain adequate hydration while on doxycycline, as it helps mitigate some gastrointestinal side effects. Avoid taking the medication with dairy products, calcium supplements, or antacids, as these may decrease its absorption. Use sun protection to reduce the risk of photosensitivity reactions.
When prescribed for a uterine infection, follow the treatment regimen closely. Report any unexpected symptoms or side effects to your healthcare professional promptly for proper evaluation and management.