If you are managing type 2 diabetes, consider incorporating Glipizide 10 mg tablets into your treatment plan. Glipizide works by stimulating your pancreas to produce more insulin, effectively lowering your blood sugar levels after meals.
Dosage plays a key role in achieving the desired results. Typically, starting with a dose of 5 mg can be beneficial, gradually increasing to 10 mg based on your physician’s advice. Regular monitoring of blood glucose is essential to assess the effectiveness of this medication and adjust the dosage if necessary.
Be aware of possible side effects, such as low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), which can occur if meals are skipped or intake is not balanced. It’s wise to carry a source of sugar, like glucose tablets, to manage any sudden drops in blood sugar levels. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making changes to your medication regimen.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise complements the use of Glipizide, enhancing its effectiveness in managing your diabetes. Follow your healthcare team’s recommendations closely for the best outcomes.
- Glipizide 10 mg Tablets: A Comprehensive Overview
- What is Glipizide 10 mg?
- Dosage and Administration
- Possible Side Effects
- Mechanism of Action of Glipizide
- Key Actions
- Additional Effects
- Dosage Guidelines for Glipizide 10 mg
- Administration
- Monitoring
- Potential Side Effects of Glipizide
- Hypoglycemia
- Allergic Reactions
- Drug Interactions with Glipizide
- Common Drug Interactions
- Other Considerations
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels While on Glipizide
- Patient Considerations and Warnings for Glipizide Use
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
- Potential Risks and Side Effects
Glipizide 10 mg Tablets: A Comprehensive Overview
Glipizide 10 mg tablets serve as a critical component in managing type 2 diabetes by enhancing insulin secretion from the pancreas. Administer these tablets to individuals as prescribed by healthcare providers, typically 30 minutes before meals to optimize blood sugar control.
Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on individual blood glucose levels, tolerance, and response. Regular monitoring ensures effective management of diabetes. Common starting dosages include 2.5 mg to 5 mg, escalating to 10 mg when necessary.
Side effects can include hypoglycemia, nausea, and diarrhea. Ensure patients are informed about recognizing hypoglycemic symptoms, such as sweating, dizziness, and confusion. It’s crucial to keep fast-acting sugar sources handy, such as glucose tablets or sugary drinks.
| Potential Side Effects | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Hypoglycemia | Monitor blood sugar; have quick glucose sources available. |
| Nausea | Consider taking with food; consult a doctor if persistent. |
| Diarrhea | Stay hydrated; report prolonged issues to a healthcare provider. |
Drug interactions may occur, especially with other diabetes medications, aspirin, and alcohol. Regular consultations with healthcare providers can prevent complications. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss potential risks and alternative treatments with their doctors.
Lifestyle modifications, alongside medication, enhance outcomes. Encourage a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management to maximize the benefits of Glipizide. Anticipate ongoing assessments to adjust treatment plans as needed.
What is Glipizide 10 mg?
Glipizide 10 mg is an oral medication used to manage blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It belongs to the class of drugs known as sulfonylureas, which stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin, thereby lowering blood glucose. This medication is usually prescribed when diet and exercise alone do not yield adequate control of blood sugar levels.
Dosage and Administration
Patients typically take Glipizide 10 mg once daily, about 30 minutes before a meal. It’s essential to follow the prescribing doctor’s instructions regarding dosage adjustments based on blood sugar readings.
Possible Side Effects
Common side effects associated with Glipizide include:
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Weight gain
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
More serious side effects may include allergic reactions. Any unusual symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider promptly.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for those taking Glipizide to ensure optimal results and make necessary adjustments. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making changes to your medication regimen.
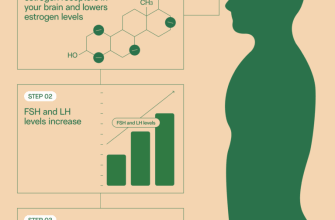
Mechanism of Action of Glipizide
Glipizide stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. This process decreases blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Key Actions
- Inhibits ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the pancreatic beta-cell membrane.
- Leads to membrane depolarization and opening of voltage-gated calcium channels.
- Increased intracellular calcium triggers insulin release.
Additional Effects
- Enhances insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
- Reduces hepatic glucose production.
Overall, Glipizide effectively lowers blood sugar by promoting insulin release while also improving the body’s response to insulin. This dual action supports better glycemic control for individuals managing type 2 diabetes.
Dosage Guidelines for Glipizide 10 mg
For most adults, the usual starting dose is 5 mg taken orally before meals. Depending on blood sugar levels, healthcare providers may adjust the dosage. The maximum recommended daily dose is 20 mg.
Administration
Swallow the Glipizide tablet whole with a glass of water. Avoid crushing or chewing the tablet. Take it approximately 30 minutes before a meal to enhance its effectiveness.
Monitoring
Regularly monitor blood glucose levels to track response to the medication. Schedule follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to evaluate dosage effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Adjustments may be required for older adults or those with kidney or liver issues. Inform your healthcare provider if you experience symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as dizziness or sweating, as this may necessitate a dosage change.
Potential Side Effects of Glipizide
Glipizide can cause several side effects, and users should monitor their health closely. Common effects include dizziness, headache, and gastrointestinal issues such as nausea or diarrhea. If these symptoms persist, consult a healthcare provider.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is a significant concern for those taking Glipizide. Symptoms include sweating, trembling, rapid heartbeat, and confusion. Regular blood sugar monitoring and understanding the signs of low blood sugar are crucial. Keeping fast-acting glucose sources, like glucose tablets or juice, nearby is beneficial in case of severe drops in blood sugar levels.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, characterized by rash, itching, or swelling, particularly of the face or throat. If you notice these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. Always inform your healthcare provider about any previous drug allergies.
Other potential effects can involve weight gain and changes in liver function tests. Regular check-ups and discussing any unusual symptoms with a doctor will help in managing these concerns effectively.
Drug Interactions with Glipizide
Glipizide can interact with various medications, potentially affecting blood sugar levels. Monitor your blood glucose closely if you are taking medications such as beta-blockers, which may mask symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Common Drug Interactions
Medications such as sulfonamides, salicylates, and certain antibiotics, including chloramphenicol and fluoroquinolones, can enhance the effects of glipizide. Adjustments in your medication regimen may be necessary.
Other Considerations
Always inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Avoid alcohol, as it can increase the risk of low blood sugar. Keep communication open with your physician for optimal management of your diabetes while on glipizide.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels While on Glipizide
Regularly check your blood sugar levels to ensure they remain within your target range while taking Glipizide. Aim to monitor your levels at least once daily or as directed by your healthcare provider.
Identify times for monitoring that align with your routine. Checking blood sugar levels before meals and before bedtime offers valuable insights into how Glipizide affects your glucose control. Keep a log of your readings to spot patterns and adjust as necessary.
Be aware of symptoms that may indicate low blood sugar, such as dizziness, sweating, or confusion. Carry a source of fast-acting carbohydrates, like glucose tablets or juice, to address any hypoglycemic episodes immediately. Consult your doctor if you experience frequent low readings.
Regular communication with your healthcare provider is key. Share your blood glucose logs and discuss any difficulties you face. Your provider can help adjust your Glipizide dosage or suggest additional strategies to maintain stable levels.
Consider factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress that can influence your blood sugar. Maintain a balanced diet and incorporate regular exercise to enhance the effects of Glipizide and support overall health.
Using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can provide real-time data and trends, making it easier to adjust your lifestyle and treatment as needed. If interested, discuss this option with your doctor for tailored recommendations.
Patient Considerations and Warnings for Glipizide Use
Before starting Glipizide, ensure you inform your healthcare provider about any allergies, medical conditions, or current medications. This helps prevent potential interactions.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly check your blood glucose levels to ensure they remain within the target range. Adjusting the Glipizide dosage may be necessary based on these readings. Look for signs of hypoglycemia, such as dizziness, sweating, or confusion. Have a source of fast-acting sugar on hand, like glucose tablets, to manage these symptoms if they arise.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Glipizide may cause weight gain, making diet and exercise important parts of your management plan. Be aware of the symptoms of liver or kidney issues, such as jaundice or changes in urination, and report these to your doctor immediately. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss potential risks with their health care provider, as Glipizide may affect the baby.