For optimal results, consider starting Clomid treatment before reaching the age of 35. Studies indicate that women under this age experience a significantly higher success rate, with approximately 80-90% achieving ovulation and around 40-50% conceiving within six months of treatment. This highlights the importance of early intervention for those facing fertility challenges.
Women aged 35 to 39 show a decline in Clomid efficacy. The ovulation rates drop to about 70-80%, and the pregnancy rates fall to around 30-40%. As age increases, the quality of eggs diminishes, which impacts overall success rates. Hence, couples in this age bracket should remain proactive and consider consulting a fertility specialist.
For women aged 40 and above, the dynamics shift significantly. Clomid success rates plummet, with only 10-20% achieving ovulation and a mere 5-10% conceiving without additional assisted reproductive technologies. Women in this age range may have better outcomes with alternative fertility treatments, such as IVF, which provide more comprehensive options for conception.
In summary, awareness of age-related Clomid success rates can guide decision-making in fertility treatment. Early intervention proves crucial, and understanding one’s unique situation can facilitate targeted strategies for achieving pregnancy.
- Clomid Success Rates by Age
- Understanding Clomid and Its Mechanism of Action
- How Clomid Works
- Clomid Use and Dosage
- Clomid Success Rates for Women Under 30
- Clomid Success Rates for Women Aged 30-34
- Responding to Treatment
- Adequate Preparation
- Clomid Success Rates for Women Aged 35-39
- Factors Influencing Success
- Recommendations for Increasing Chances
- Clomid Success Rates for Women Aged 40 and Over
- Factors Influencing Clomid Success Rates Across Different Ages
- Ovarian Reserve and Egg Quality
- Timing and Dosage
- Comparative Analysis of Clomid and Other Fertility Treatments by Age
- Clomid vs. Letrozole
- Clomid vs. Injectable Gonadotropins
- Consultation and Monitoring During Clomid Treatment
Clomid Success Rates by Age
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, shows varying success rates based on age. Understanding these can help set realistic expectations for those seeking treatment.
Here are the success rates broken down by age group:
- Under 25: Approximately 50-60% of women in this age group achieve pregnancy within the first three cycles of Clomid.
- 25-30: Success rates remain high, around 40-50%, reflecting good ovarian response and egg quality.
- 31-35: The likelihood drops to about 30-40% as age impacts ovarian reserve and egg quality.
- 36-40: Here, success rates decline further to 20-30%. Fertility factors increasingly affect outcomes.
- Over 40: Women over 40 see lower rates, often less than 10%. Fertility specialists may explore other options.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to assess personal fertility health and receive tailored advice. Monitoring ovulation, adjusting dosages, and considering additional treatments may improve chances of success.
For those considering Clomid, being proactive and informed increases the likelihood of achieving desired results.
Understanding Clomid and Its Mechanism of Action
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, functions primarily as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). This medication plays a significant role in treating ovulatory dysfunction, making it a standard choice for women facing challenges in conceiving.
How Clomid Works
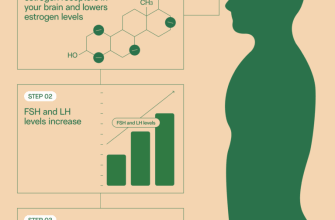
Clomid works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus. This action triggers the body to increase the production of gonadotropins, specifically follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). The surge in these hormones stimulates the ovaries, promoting follicle development and ovulation.
- Estrogen blockade leads to hypothalamic stimulation.
- Increased FSH levels encourage ovarian follicle growth.
- LH surge is crucial for the final maturation and release of eggs.
This hormonal cascade is vital for restoring regular ovulation cycles, especially in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and irregular periods.
Clomid Use and Dosage
Clomid is typically administered in a 5-day regimen at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Common starting doses range from 50 mg to 150 mg. Monitoring response through ultrasound and blood tests ensures effective treatment while minimizing risks.
- Begin Clomid on cycle days 3 to 5.
- Adjust dosage based on ovulation response and side effects.
- Limit usage to three to six cycles to avoid complications.
Understanding the mechanism and correct usage of Clomid can significantly enhance the chances of conception. Regular consultation with a healthcare provider ensures optimal outcomes tailored to individual needs.
Clomid Success Rates for Women Under 30
Women under 30 generally experience higher success rates with Clomid. Reports indicate that approximately 80% of women in this age group will ovulate after completing a cycle of treatment. Ovulation typically occurs within the first few months, making timely assessments essential for optimizing chances of conception.
Among women who ovulate while using Clomid, about 30-40% achieve pregnancy within the first three cycles. This rate remains consistent, with many women conceiving within six months of starting treatment. Delay in conception past this point may warrant further evaluation by a healthcare provider.
Monitoring is crucial during Clomid therapy. Regular ultrasounds and hormone level testing can help track ovulation and diagnose any potential issues. Women under 30 should remain in close contact with their healthcare professionals throughout the treatment process.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle supports Clomid’s effectiveness. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing stress levels contribute positively to reproductive health. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can further enhance the chances of conception.
Individuals considering Clomid should engage in thorough discussions with their healthcare provider to understand treatment expectations, possible side effects, and alternative options. Making informed decisions increases the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
Clomid Success Rates for Women Aged 30-34
Women aged 30-34 experience a Clomid success rate ranging from 60% to 70% in achieving pregnancy within six cycles of treatment. Factors influencing these rates include ovarian reserve, underlying fertility issues, and overall health. Regular monitoring through ultrasounds and hormone level assessments enhances the effectiveness of Clomid therapy.
Responding to Treatment
Women in this age group often respond well to Clomid, with the majority experiencing ovulation within the first few cycles. It’s crucial to adhere to the prescribed dosage and attend follow-up appointments to track progress. If ovulation occurs but pregnancy does not, fertility specialists may suggest increasing the dosage or exploring additional treatments.
Adequate Preparation
Preparing for Clomid treatment involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and addressing any medical issues. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful substances contribute positively to overall fertility. Women should also consult with healthcare providers to evaluate any additional factors that could impact fertility success.
Clomid Success Rates for Women Aged 35-39
Women aged 35-39 can experience success rates with Clomid ranging from 20% to 30% per cycle. This age group often faces unique challenges due to a natural decline in fertility. However, many women in this age bracket have successfully conceived while using Clomid, especially when combined with monitoring by a specialist.
Factors Influencing Success
Several factors play a significant role in determining Clomid’s effectiveness for women in this age group. Ovulation status is critical; those who ovulate regularly tend to have higher success rates. Additionally, the presence of underlying conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can enhance the likelihood of response to treatment. Regular monitoring through ultrasounds and hormone assessments assists in optimizing timing and dosage, further increasing the chances of success.
Recommendations for Increasing Chances
To improve outcomes, consider lifestyle modifications. Maintaining a healthy weight, optimizing diet, and engaging in regular physical activity enhance overall reproductive health. Consultation with a fertility specialist provides tailored advice and additional options, such as hormonal support or assisted reproductive technologies, if Clomid does not lead to pregnancy after several cycles. Regular follow-up appointments ensure that treatment is adjusted based on individual response.
Clomid Success Rates for Women Aged 40 and Over
Women aged 40 and over seeking to conceive with Clomid can expect varying success rates compared to younger counterparts. Data indicates that these rates tend to be lower due to age-related factors affecting ovarian function and egg quality.
The success rate of Clomid treatments in this age group ranges from 5% to 10% per cycle. These statistics highlight that while Clomid can help stimulate ovulation, the probability of achieving pregnancy decreases as age increases. Specific research shows that women over 40 may require higher doses or additional treatments to enhance their chances.
It’s essential to monitor ovarian response through ultrasounds and hormone tests. This way, you can adjust the treatment plan as needed for optimal results. Many healthcare providers recommend combining Clomid with lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tobacco use, which can improve outcomes.
| Age Group | Estimated Success Rate per Cycle |
|---|---|
| Under 35 | 15% – 20% |
| 35 – 39 | 10% – 15% |
| 40 and Over | 5% – 10% |
Consulting with a fertility specialist can provide personalized insight and treatment options that fit your health profile. Understanding the risks and realistic expectations leads to informed decision-making in the pursuit of pregnancy with Clomid at this age.
Factors Influencing Clomid Success Rates Across Different Ages
Success rates of Clomid vary significantly by age due to several key factors. Younger women, particularly those under 35, generally experience higher success rates, often exceeding 80% in achieving ovulation. This is largely due to better ovarian reserve and more responsive hormonal profiles. In contrast, women over 35 see a decline in success, with rates dropping to approximately 40-60% as age-related factors impact fertility quality.
Hormonal balance plays a crucial role. Younger women usually have a more stable hormonal environment, which aids in ovulation induction. As age increases, hormonal fluctuations can lead to irregular cycles that reduce Clomid’s efficacy. Polycycstic ovary syndrome (PCOS) also influences outcomes; younger women with PCOS respond well to Clomid, while older patients may face additional challenges linked to age-related complications.
Ovarian Reserve and Egg Quality
The decline in ovarian reserve is a significant factor affecting older women. Clomid may not be sufficient if there are underlying issues with egg quality. While younger women with a higher number of viable eggs respond positively to treatment, older women may require additional interventions, such as assisted reproductive technologies, to achieve pregnancy.
Timing and Dosage
Timing of Clomid cycles can also impact success rates. Younger women are often more likely to time intercourse around ovulation effectively, maximizing their chances. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for older women, as individualized treatment can enhance response and outcomes. Consultation with a fertility specialist can provide tailored recommendations based on age and specific health conditions.
Comparative Analysis of Clomid and Other Fertility Treatments by Age
Women under 35 often experience higher success rates with Clomid, reaching approximately 80% ovulation and 30-40% pregnancy rates per cycle. For those between 35 and 39, ovulation rates remain around 70%, while pregnancy rates drop to around 15-20% per cycle. In contrast, women over 40 see significantly reduced chances, with ovulation at approximately 30% and pregnancy rates sinking below 5% per cycle.
Clomid vs. Letrozole
Letrozole has emerged as an alternative to Clomid, particularly for women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Research shows that Letrozole produces comparable ovulation rates in women under 35 while outperforming Clomid in pregnancy rates, especially for those aged 35-39. The overall efficacy of Letrozole tends to be better for this demographic, making it a viable option for those who may not respond well to Clomid.
Clomid vs. Injectable Gonadotropins
For women over 35 or those with unexplained infertility, injectable gonadotropins typically offer higher success rates. These treatments can stimulate the ovaries more directly, resulting in ovulation rates of over 90% and pregnancy rates exceeding 30% in favorable cases. This option proves particularly beneficial for older women who may have diminished ovarian reserve but still wish to conceive.
Each treatment option presents its unique pros and cons. Clomid remains a first-line therapy due to its affordability and ease of use, while other treatments can provide substantial benefits for specific age groups or conditions. Consulting a fertility specialist can help tailor the right approach based on individual circumstances and age.
Consultation and Monitoring During Clomid Treatment
Consult with your healthcare provider before starting Clomid. Discuss your medical history, current medications, and any underlying conditions affecting fertility. A thorough evaluation ensures personalized treatment and addresses potential risk factors.
During treatment, attend regular follow-up appointments. These visits typically occur every 1-2 months and allow your doctor to assess response to the medication. Monitoring often includes blood tests to measure hormone levels and ultrasound examinations to check for ovarian response.
Your healthcare provider may adjust the dosage based on your response. Pay attention to any side effects, such as hot flashes, mood swings, or visual disturbances, and report these to your doctor promptly. Early intervention can help manage discomfort and optimize treatment outcomes.
Document any menstrual changes and symptoms in a journal. This information aids your doctor in making informed decisions regarding the treatment plan. Clear communication fosters a collaborative environment where adjustments can be made effectively.
Consider discussing lifestyle factors that may influence fertility. Topics such as diet, exercise, and stress management can play a significant role in treatment success. Your provider can offer guidance tailored to your specific needs.
By actively participating in consultations and monitoring, you enhance your chances of achieving desired outcomes during Clomid treatment. Staying informed and engaged promotes a supportive relationship with your healthcare team, ultimately benefiting your fertility journey.